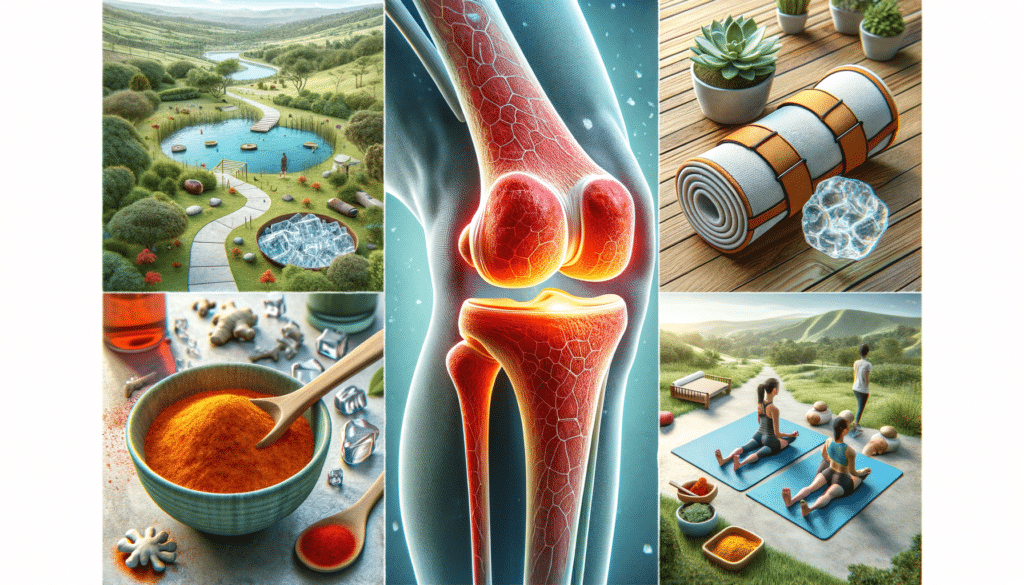
Understanding Knee Arthritis: A Closer Look
Knee arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It primarily occurs when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint wears down over time, resulting in bone-on-bone contact. This degenerative process can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities. There are various types of arthritis that can affect the knee, with osteoarthritis being the most prevalent. Rheumatoid arthritis and post-traumatic arthritis are other forms that can also contribute to knee pain.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the gradual wear and tear of cartilage, often associated with aging, obesity, and previous joint injuries. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the synovium, leading to inflammation and joint damage. Post-traumatic arthritis develops after an injury to the knee, such as a fracture or ligament tear, which can accelerate the degeneration of cartilage.
Understanding the type of arthritis affecting the knee is crucial for determining the most appropriate pain relief strategies. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and slow down the progression of the disease. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs can provide valuable insights into the condition of the knee joint.
Non-Surgical Pain Relief Options
For many individuals with knee arthritis, non-surgical interventions can offer significant relief and improve quality of life. These methods focus on reducing pain, inflammation, and stiffness while enhancing joint function. Physical therapy is one of the most effective non-surgical treatments, involving exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance balance.
Another widely used approach is medication. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or corticosteroid injections for more severe pain.
Weight management plays a crucial role in knee arthritis pain relief. Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, exacerbating pain and accelerating cartilage wear. Losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility.
Additional non-surgical options include the use of assistive devices such as knee braces or orthotic shoe inserts, which can provide support and reduce strain on the knee. Heat and cold therapy, acupuncture, and supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin are also popular among individuals seeking alternative pain relief methods.
Surgical Interventions: When Are They Necessary?
While non-surgical treatments can be effective for many, some individuals may require surgical intervention to manage knee arthritis pain. Surgery is typically considered when conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief or when the joint damage is severe. Several surgical options are available, each with its own benefits and considerations.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the removal of damaged cartilage or bone fragments from the knee joint. This can help alleviate pain and improve joint function. However, its effectiveness may be limited in cases of advanced arthritis.
Partial knee replacement, or unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, involves replacing only the damaged portion of the knee joint. This procedure is suitable for individuals with arthritis confined to a specific area of the knee. It offers a quicker recovery time compared to total knee replacement.
Total knee replacement, or total knee arthroplasty, is recommended for individuals with extensive joint damage. This procedure involves replacing the entire knee joint with an artificial implant, providing significant pain relief and improved mobility. Recovery from total knee replacement can take several months, and rehabilitation is crucial for optimal outcomes.
It’s important for individuals considering surgery to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. Factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle should be taken into account when deciding on the most appropriate surgical intervention.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Relief
Incorporating lifestyle modifications can play a pivotal role in managing knee arthritis pain and improving overall joint health. Regular exercise is essential for maintaining joint flexibility and strengthening the muscles that support the knee. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking are highly recommended, as they minimize stress on the joints while enhancing cardiovascular fitness.
Adopting a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can also contribute to pain relief. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation and support overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit individuals with arthritis.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for minimizing stress on the knee joints. Even a small amount of weight loss can lead to noticeable improvements in pain and mobility. Engaging in regular physical activity and making mindful dietary choices can support weight management efforts.
Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals cope with the emotional and physical challenges of living with arthritis. These practices promote relaxation and may reduce pain perception.
Additionally, ensuring adequate rest and sleep is vital for joint recovery and overall well-being. Creating a comfortable sleep environment and establishing a regular sleep routine can contribute to better sleep quality and enhanced pain management.
Exploring Alternative Therapies
Beyond conventional treatments, many individuals seek alternative therapies to complement their knee arthritis pain management strategies. These therapies can offer additional benefits and may be particularly appealing to those looking for holistic approaches to health.
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote healing. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help reduce pain and improve function in individuals with knee arthritis.
Herbal remedies and dietary supplements are also popular among those seeking natural pain relief. Supplements such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and turmeric have been studied for their potential anti-inflammatory effects. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, as they may interact with medications or have side effects.
Chiropractic care and massage therapy are other alternative therapies that may offer relief for some individuals. These treatments focus on improving joint alignment, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing overall well-being.
While alternative therapies can be beneficial, they should be used in conjunction with traditional medical treatments and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It’s essential to ensure that any chosen therapy is safe and appropriate for the individual’s specific condition.