Prefabricated Homes
Introduction to Prefabricated Housing
In recent years, the construction industry has witnessed a significant shift toward more efficient and cost-effective building methods. Prefabricated housing, often referred to as prefab homes, has emerged as a noteworthy solution in this context. These homes are constructed off-site in controlled environments and then transported to their final location for assembly. This innovative approach not only reduces construction time but also minimizes waste and environmental impact. As urban populations continue to grow and housing demands increase, prefabricated housing offers a viable alternative to traditional construction methods.
The Economic Benefits of Prefabricated Homes
One of the primary advantages of prefabricated housing is its affordability. By manufacturing homes in a factory setting, builders can significantly reduce costs associated with labor and materials. Bulk purchasing of materials and streamlined processes contribute to these savings, which are often passed on to the consumer. Additionally, the speed of construction is a major factor in cost reduction. Traditional building methods can take months or even years, while prefabricated homes can be completed in a matter of weeks. This efficiency not only reduces labor costs but also allows homeowners to move in sooner, potentially saving on temporary housing expenses.
Moreover, the predictability of costs in prefabricated housing is a strong selling point. Unlike traditional construction projects, which can be subject to delays and unforeseen expenses, prefab homes offer a fixed price from the outset. This financial transparency is appealing to both individual buyers and developers looking to manage budgets more effectively.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Prefabricated housing is often lauded for its eco-friendly attributes. The controlled environment of a factory setting allows for precise construction, reducing waste significantly compared to on-site building. Materials can be reused and recycled more efficiently, and the overall carbon footprint of the construction process is minimized. Furthermore, many prefab homes are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Features such as high-quality insulation, energy-efficient windows, and sustainable materials are commonly incorporated, reducing the long-term environmental impact of the home.
In addition to construction benefits, the modular nature of prefabricated homes allows for easy upgrades and modifications, further extending their lifespan and reducing the need for new resources. This adaptability is particularly important in an era where sustainability is a key consideration for many homeowners.
Design Flexibility and Customization
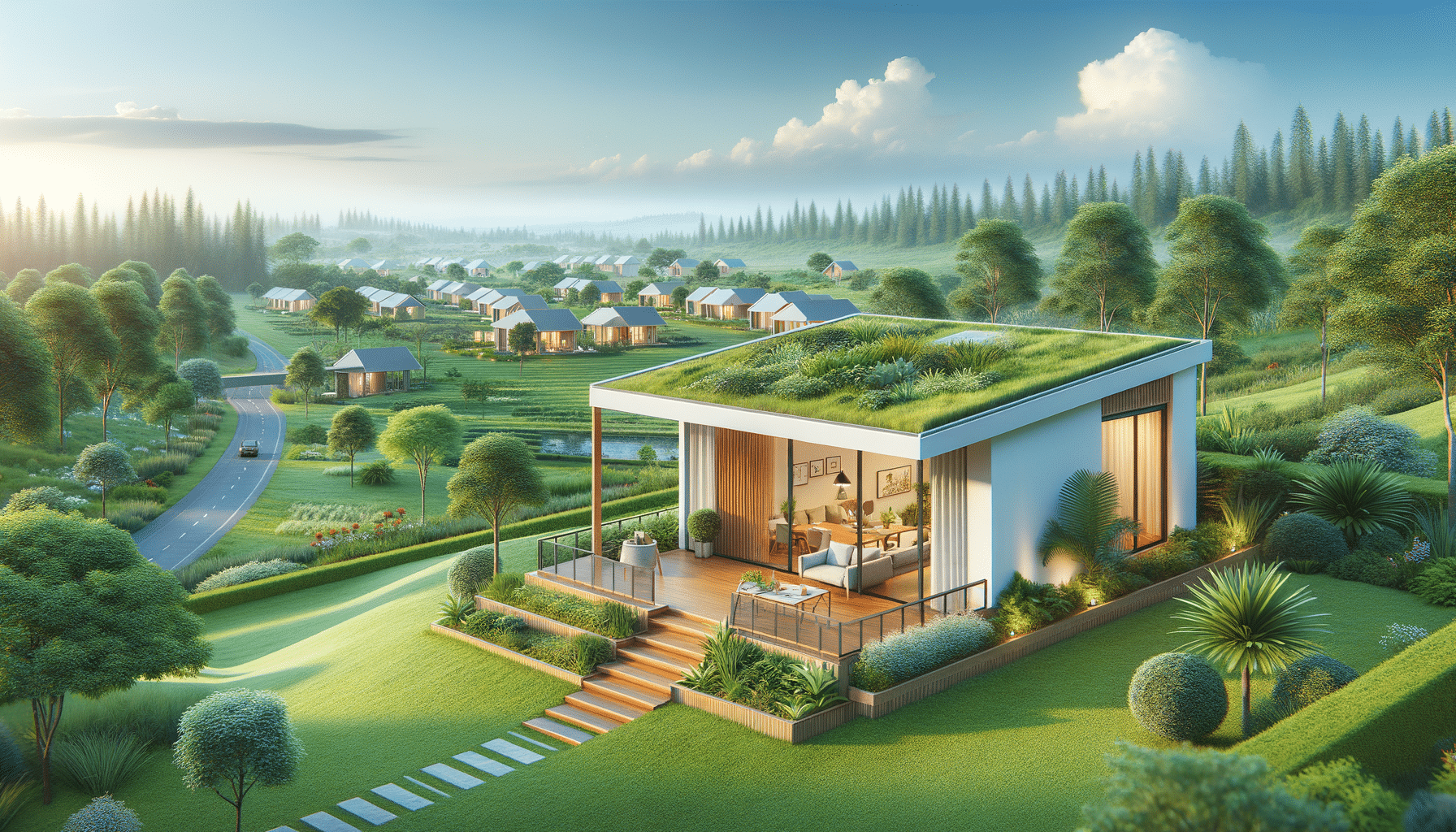
Contrary to some misconceptions, prefabricated homes offer a high degree of design flexibility and customization. Advances in technology and manufacturing have enabled a wide range of styles, sizes, and layouts to suit diverse tastes and needs. Homeowners can choose from various architectural designs, finishes, and features, ensuring that their prefabricated home aligns with personal preferences and lifestyle requirements.
The modular construction of prefab homes also allows for future expansions or alterations with minimal disruption. This flexibility is particularly appealing to young families or individuals who anticipate changes in their living situation. By choosing a prefabricated home, they can enjoy a personalized living space that can evolve with them over time.
Challenges and Considerations
While prefabricated housing offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the availability of suitable land for these homes. Zoning laws and land use regulations can sometimes pose obstacles to the placement of prefab homes, particularly in urban areas. Additionally, the perception of prefabricated homes as being of lower quality or less durable than traditional homes persists, despite advancements in construction techniques and materials.
Potential buyers should also consider the logistics of transportation and assembly. While the construction process is expedited, the delivery and installation of prefabricated homes require careful planning and coordination. It is essential to work with experienced professionals to ensure a smooth transition from factory to site.
Despite these challenges, the rise of prefabricated housing continues, driven by its affordability, efficiency, and environmental benefits. As technology advances and public perception shifts, prefab homes are poised to become a more prominent feature of the housing landscape.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Housing
Prefabricated housing represents a promising solution to the growing demand for affordable and sustainable living spaces. By combining cost efficiency, environmental responsibility, and design flexibility, these homes offer a compelling alternative to traditional construction methods. As the construction industry evolves, prefabricated homes are set to play an increasingly important role in addressing the challenges of modern housing. For prospective homeowners and developers alike, embracing this innovative approach could pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in residential construction.